Off-Axis Layered Displays:
Hybrid Direct-View/Near-Eye Mixed Reality with Focus Cues
Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG)
Graz University of Technology
Graz University of Technology
University of Otago
University of Hong Kong
Graz University of Technology
Stanford University
Graz University of Technology
Abstract
This work introduces off-axis layered displays, the first approach to stereoscopic direct-view displays with support for focus cues. Off-axis layered displays combine a head-mounted display with a traditional direct-view display for encoding a focal stack and thus, for providing focus cues. To explore the novel display architecture, we present a complete processing pipeline for the real-time computation and post-render warping of off-axis display patterns. In addition, we build two prototypes using a head-mounted display in combination with a stereoscopic direct-view display, and a more widely available monoscopic direct-view display. In addition we show how extending off-axis layered displays with an attenuation layer and with eye-tracking can improve image quality. We thoroughly analyze each component in a technical evaluation and present examples captured through our prototypes.
Teaser
Overview
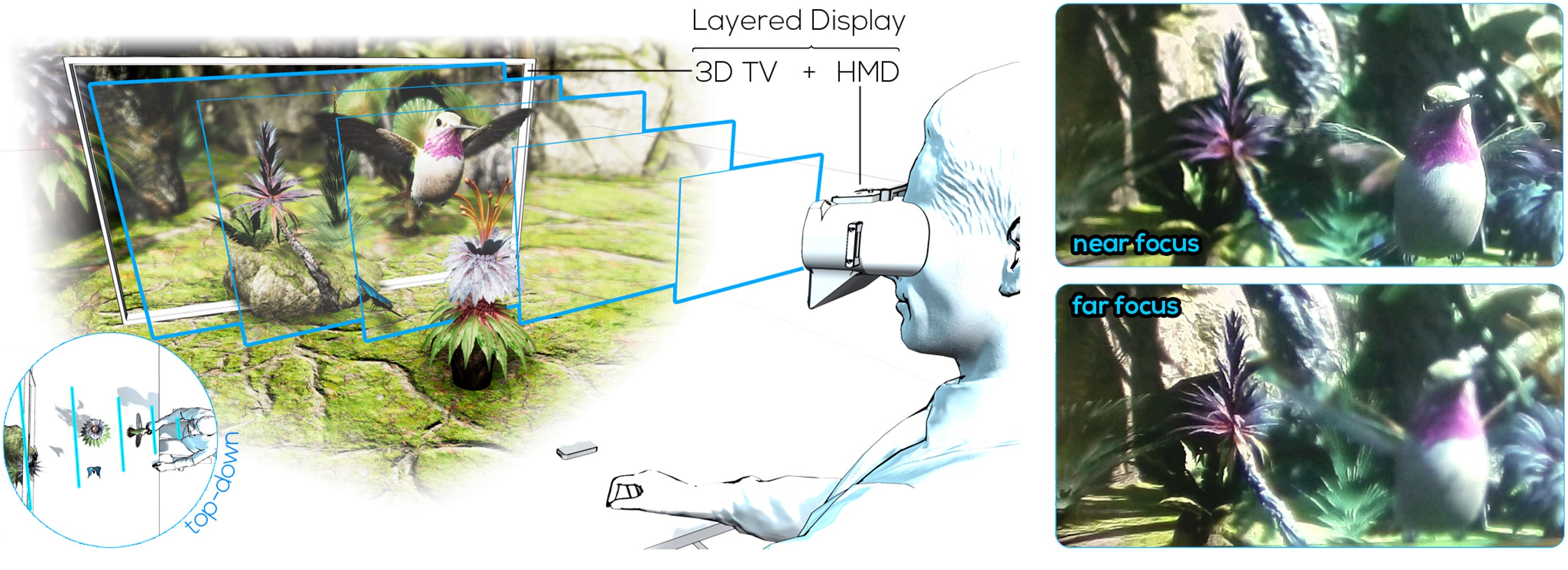
Off-axis layered displays are a type of display system that combines a traditional direct-view display with an optical see-through (OST) head-mounted display (HMD) to create a joint layered display. This allows users to focus on different objects in a scene by combining the light emitted from the direct-view display with content shown on the HMD. The wearable display plane is located 3 diopter (dpt) in front of the user, providing a viewing volume from approximately 30 cm to the direct-view display, which is typically placed at a distance of 1.5-2 m in a common setting. It's worth noting that the volume size can be adjusted interactively based on the distance between the user and the direct-view displays. By combining a stationary and a head-worn display layer, off-axis layered displays can be used in scenarios where existing display technology can be repurposed. For example, users who purchase a see-through HMD may have access to large format direct-view displays in typical office environments or homes. When synchronized, these independent displays can be used for 3D viewing with focus cues that the HMD or stationary display cannot provide in standalone mode. As a result, off-axis layered displays offer many opportunities for professional and casual applications that can benefit from enhanced visual perception, such as authoring and viewing geometric and CAD data, spatial telepresence, immersive movies, games, and simulations in desktop, home, and CAVE-like environments.
Through-the-Lens Results
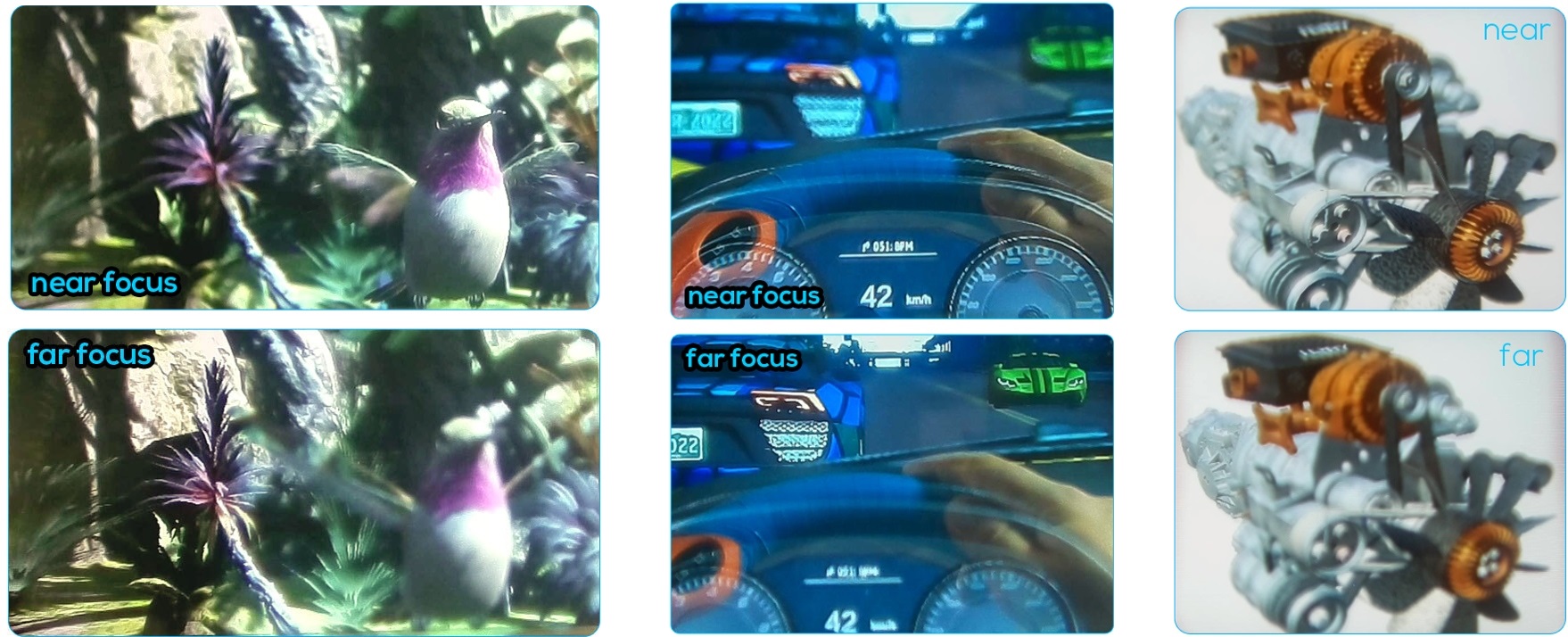

Through-the-lens results of three different scenes captured through our prototype. In the top row, the camera was focused to a close distance, and the bottom row shows far focus.
Citation
@article{ebner2023offaxis,
author={Ebner, Christoph and Mohr, Peter and Langlotz, Tobias and Peng, Yifan and Schmalstieg, Dieter and Wetzstein, Gordon and Kalkofen, Denis},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
title={Off-Axis Layered Displays: Hybrid Direct-View/Near-Eye Mixed Reality with Focus Cues},
year={2023}
}